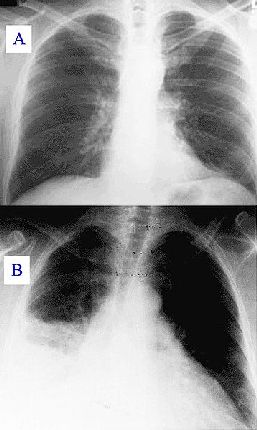
What is pneumonia? Pneumonia is a lung disease caused by different viruses and bacteria. The most common type is a bacterium called pneumococcal pneumonia or bacterial pneumonia. Each year the state united thousands of adults to develop bacterial pneumonia, most of them elderly. Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics and most people will be better once treated. However, some bacteria that cause disease is becoming stronger and can not be easily cured with antibiotics. Approximately 30 percent of people with pneumonia, the disease spreads to the blood, lungs, middle ear, or nervous system and lead to serious health problems and / or death. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention more than 50,000 adults died of pneumonia in 2006. The most important cheap strattera thing to know about pneumococcal pneumonia is what prevented with vaccines disease. You can get pneumonia as a result of contact with sick people or to keep the bacteria that cause it. Very small droplets sprayed into the air as an infected person sneezes or coughs says the spread of infection. Some people can carry the bacteria in the throat without being sick. You can get sick very quickly with bacterial pneumonia. Symptoms may include:
If you have any of these symptoms you should go to the doctor. The sooner you have treatment, the faster you will recover. Why is it important to be vaccinated? It is very important for some people to vaccination. Bacterial pneumonia is a serious disease that kills thousands every year older. The vaccine has done a good job in those vaccinated to prevent severe disease, hospitalization and death associated with bacterial infection pneumonia. It makes sense to be vaccinated for those who have a high risk of contracting disease. Those who have chronic health problems (such as kidney disease, heart disease, etc.)
Any resident or most people will need only one shot in their lives. Some need a power shot. However, you should never have more than two shots of vaccine pneumonia in your life, and those shots should be given not less than five years apart. Lee shot cause side effects? After this shot you may have redness and pain in the area where you had a shot (mild local reactions). Rarely (less than 1% of cases), fever, muscle aches, or severe local reactions. You can not get pneumococcal infection from the shot. Talk to your doctor before you shot if you have any of the above. Medicare to pay for the vaccine and that it will cost me? Yes
cover the cost of pneumonia vaccination for people covered by Medicare. Your cost will be $ 0 if your doctor accepts assignment. The advantage is covered. If you have medical care, and
and Medicare covers 100% need not apply to Medigap plan details, so as not to be forwarded to Medigap plan copay to pay. It is only if Medicare Part B covers 100% of the cost. Thus, no copay. However, if Medicare Part B covers only 80% of Medigap plan must pay for all or almost 20% after Medicare pays its part. In terms of Medicare Advantage, you must call agent. Where can I get a pneumonia shot? Most people get pneumonia shot by your doctor or health care providers. Your doctor must write to the vaccine in order to subject your benefits Medicare. If you get the benefits of life help you to take a picture in your home or with the object of life. Can I have a pneumonia shot at the same time as the flu shot? Yes you can. However, you need a flu shot every year, and most of all, you need only one shot pneumonia. One shot for pneumonia good life for most people. When should I get my shot pneumonia? Unlike the flu which is available only from October to March, pneumonia shots are available year round and you can get them at any time of year. .